构建可靠的分布式应用程序可能会面临许多挑战。系统崩溃、网络故障以及进程在执行过程中可能会出现卡顿。这正是 Temporal 发挥作用的地方。它是一个开源的工作流编排平台。当与 Spring Boot 结合使用时,它能够帮助您构建强大的应用程序,这些应用程序能够应对现实世界中的各种挑战。
为什么需要 Temporal?
如果您曾经使用过分布式系统,您可能会遇到流程故障。这些故障可能导致系统不一致。
例如,它们可能处理了付款但未更新订单,或者发送了一封电子邮件却没有更新数据库。Temporal 可以解决这些问题,它提供持久执行、自动重试和状态管理功能。
Spring Boot + Temporal 为您提供了处理复杂流程的工具,同时保留了您熟悉的 Spring 生态系统。您可以享受两者的优势,既能获得 Spring 的依赖注入和配置功能,又能享受到 Temporal 的工作流管理能力。
设置环境
在我们详细分析代码之前,首先需要配置我们的开发环境。我们需要两个要素:一个包含 Temporal 依赖项的 Spring Boot 应用程序,以及一个正在运行的 Temporal 服务器。
首先,让我们创建具有必要依赖项的项目:
pom.xml :
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>3.4.0</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>me.vrnsky</groupId>
<artifactId>temporal-spring-boot</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>temporal-spring-boot</name>
<description>temporal-spring-boot</description>
<properties>
<java.version>17</java.version>
<temporal.version>1.17.0</temporal.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.temporal</groupId>
<artifactId>temporal-sdk</artifactId>
<version>${temporal.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.micrometer</groupId>
<artifactId>micrometer-registry-prometheus</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<annotationProcessorPaths>
<path>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.18.32</version>
</path>
</annotationProcessorPaths>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<excludes>
<exclude>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</exclude>
</excludes>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>接下来,我们需要一个正在运行的 Temporal 服务器。
使用 Docker 开始最简单:
version: '3.5'
services:
postgresql:
image: postgres:13
environment:
POSTGRES_USER: temporal
POSTGRES_PASSWORD: temporal
ports:
- "5432:5432"
networks:
- temporal-network
temporal:
image: temporalio/auto-setup:1.20.0
depends_on:
- postgresql
environment:
- DB=postgresql
- DB_PORT=5432
- POSTGRES_USER=temporal
- POSTGRES_PWD=temporal
- POSTGRES_SEEDS=postgresql
ports:
- "7233:7233"
networks:
- temporal-network
temporal-web:
image: temporalio/web:1.15.0
environment:
- TEMPORAL_GRPC_ENDPOINT=temporal:7233
- TEMPORAL_PERMIT_WRITE_API=true
ports:
- "8088:8088"
depends_on:
- temporal
networks:
- temporal-network
networks:
temporal-network:
driver: bridgeTemporal 的工作原理
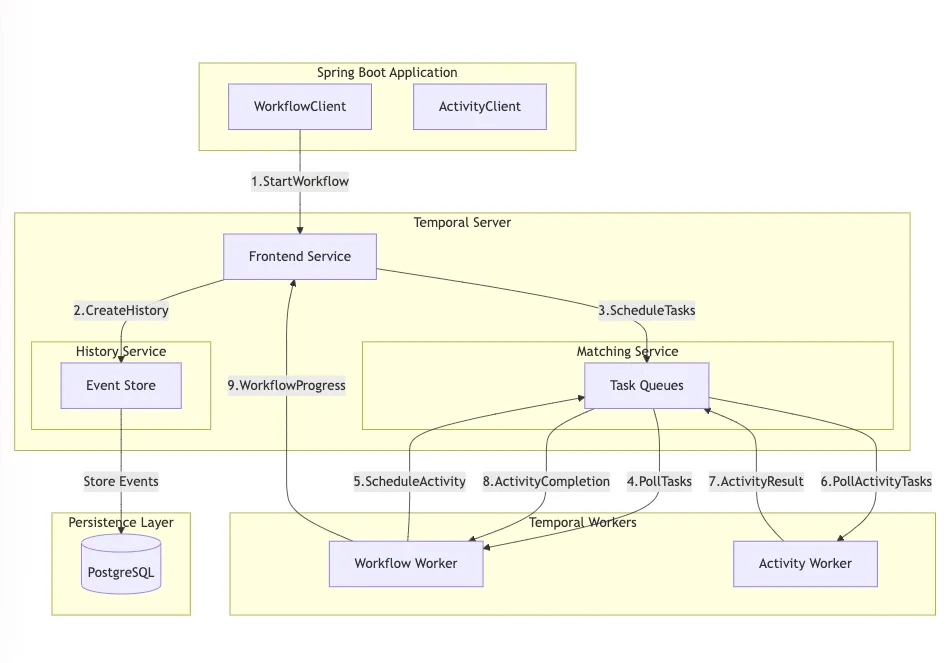
将 Temporal 看作是一个复杂的任务管理器,用于分布式进程。当您的 Spring Boot 应用程序需要启动工作流时,它会通过 WorkflowClient 与 Temporal 进行通信。随后,Temporal 会管理整个流程,确保每个步骤都能成功完成。即使在系统崩溃或网络故障的情况下,它也能维护工作流的状态。
案例学习
让我们来构建一个实用的系统——订单处理系统。这是一个常见的应用场景,可能会出现很多问题:付款可能失败、库存可能不足或运输服务可能暂停。工作流程将如下所示:
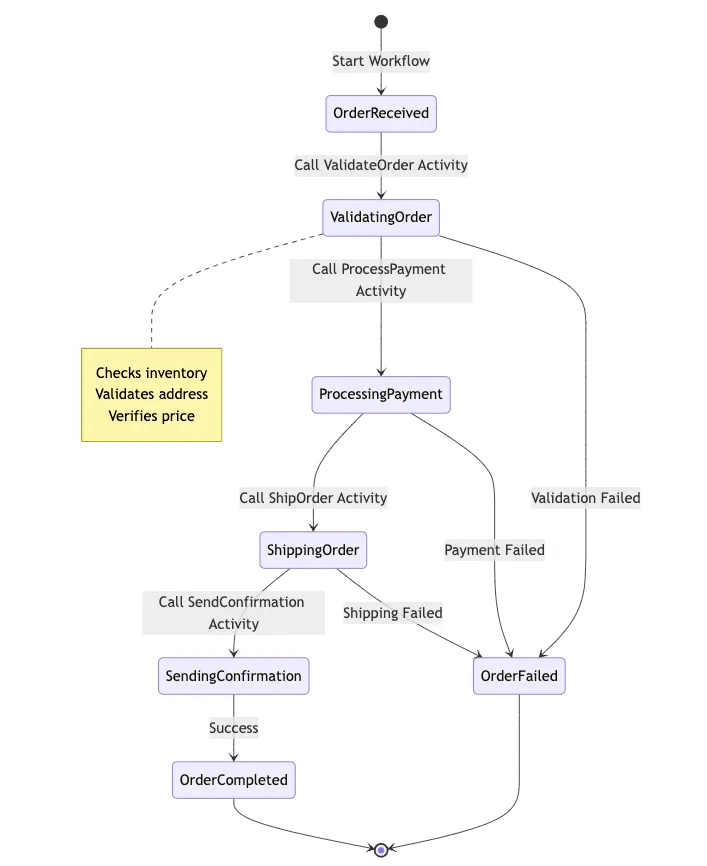
现在,让我们将此工作流放入代码中
import io.temporal.workflow.WorkflowInterface;
import io.temporal.workflow.WorkflowMethod;
@WorkflowInterface
public interface OrderProcessingWorkflow {
@WorkflowMethod
void processOrder(String orderId);
}import io.temporal.activity.ActivityInterface;
@ActivityInterface
public interface OrderActivity {
void validateOrder(String orderId);
void processPayment(String orderId);
void shipOrder(String orderId);
void sendConfirmation(String orderId);
}这是工作流程的实现。
import io.temporal.activity.ActivityOptions;
import io.temporal.workflow.Workflow;
import me.vrnsky.temporalspringboot.activity.OrderActivity;
import java.time.Duration;
public class OrderProcessWorkflowImpl implements OrderProcessingWorkflow {
private final ActivityOptions options = ActivityOptions.newBuilder()
.setScheduleToCloseTimeout(Duration.ofMinutes(5))
.build();
private final OrderActivity orderActivity = Workflow.newActivityStub(OrderActivity.class, options);
@Override
public void processOrder(String orderId) {
try {
orderActivity.validateOrder(orderId);
orderActivity.processPayment(orderId);
orderActivity.shipOrder(orderId);
orderActivity.sendConfirmation(orderId);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw e;
}
}
}我们还需要实现活动界面并配置 Workflow 客户端。
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
@Slf4j
public class OrderActivityImpl implements OrderActivity {
@Override
public void validateOrder(String orderId) {
log.info("Validating order {}", orderId);
}
@Override
public void processPayment(String orderId) {
log.info("Processing payment {}", orderId);
}
@Override
public void shipOrder(String orderId) {
log.info("Shipping order {}", orderId);
}
@Override
public void sendConfirmation(String orderId) {
log.info("Sending confirmation {}", orderId);
}
}import io.temporal.client.WorkflowClient;
import io.temporal.serviceclient.WorkflowServiceStubs;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class TemporalConfig {
@Bean
public WorkflowClient workflowClient() {
WorkflowServiceStubs service = WorkflowServiceStubs.newLocalServiceStubs();
return WorkflowClient.newInstance(service);
}
}此时,我们可以添加一个 Controller,并通过手动过程测试我们的工作流程。
import io.temporal.client.WorkflowClient;
import io.temporal.client.WorkflowOptions;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import me.vrnsky.temporalspringboot.workflow.OrderProcessingWorkflow;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class OrderController {
private final WorkflowClient workflowClient;
@PostMapping("/orders/{orderId}/process")
public ResponseEntity<String> processOrder(@PathVariable String orderId) {
OrderProcessingWorkflow workflow = workflowClient.newWorkflowStub(
OrderProcessingWorkflow.class,
WorkflowOptions.newBuilder()
.setTaskQueue("OrderProcessingQueue")
.setWorkflowId("Order-" + orderId)
.build());
WorkflowClient.start(workflow::processOrder, orderId);
return ResponseEntity.accepted().body("Order processing started");
}
}使用以下 cURL 命令发送请求测试一下:
curl -X POST http://localhost:8080/orders/1/process
可以看到 Order processing started 的请求响应。同时,在 Web UI 中,您应该会看到工作流正在运行:
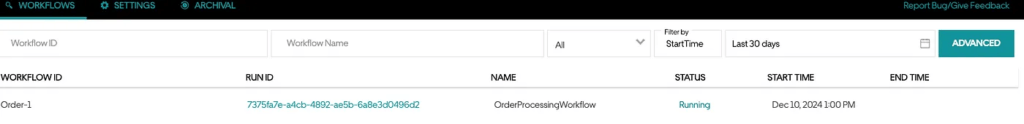
由于没有工作程序来轮询和执行工作流程,因此工作流程一直在运行。让我们添加一个新的 worker。
import io.temporal.client.WorkflowClient;
import io.temporal.worker.Worker;
import io.temporal.worker.WorkerFactory;
import me.vrnsky.temporalspringboot.activity.OrderActivityImpl;
import me.vrnsky.temporalspringboot.workflow.OrderProcessWorkflowImpl;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class OrderWorker {
private final Worker worker;
public OrderWorker(WorkflowClient workflowClient) {
WorkerFactory factory = WorkerFactory.newInstance(workflowClient);
this.worker = factory.newWorker("OrderProcessingQueue");
worker.registerWorkflowImplementationTypes(OrderProcessWorkflowImpl.class);
worker.registerActivitiesImplementations(new OrderActivityImpl());
factory.start();
}
}现在,如果您再次运行 Spring Boot 应用程序,您应该会看到工作流已完成。
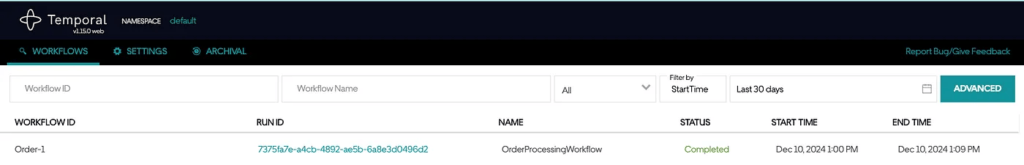
这种实现的好处在于 Temporal 为您解决了分布式系统中的所有复杂问题。如果任何活动出现失败,Temporal 会根据您的配置对该活动进行重试。如果您的应用程序在处理过程中崩溃,Temporal 会在您重新启动时从上次中断的地方继续。
失败处理
让我们再优化下工作流,以包含补偿逻辑
import io.temporal.workflow.QueryMethod;
import io.temporal.workflow.SignalMethod;
import io.temporal.workflow.WorkflowInterface;
import io.temporal.workflow.WorkflowMethod;
import me.vrnsky.temporalspringboot.model.OrderResult;
import me.vrnsky.temporalspringboot.model.OrderStatus;
@WorkflowInterface
public interface OrderProcessingWorkflow {
@WorkflowMethod
OrderResult processOrder(String orderId);
@QueryMethod
OrderStatus getOrderStatus();
@SignalMethod
void cancelOrder(String reason);
}public record OrderResult(
String orderId,
OrderStatus status,
String message
) {
}public enum OrderStatus {
CREATED,
VALIDATED,
PAYMENT_PROCESSED,
SHIPPED,
COMPLETED,
FAILED,
COMPENSATING,
CANCELLED
}public enum AlertLevel {
INFO,
WARNING,
ERROR,
CRITICAL
}import io.temporal.activity.ActivityInterface;
import me.vrnsky.temporalspringboot.model.AlertLevel;
import me.vrnsky.temporalspringboot.model.OrderStatus;
@ActivityInterface
public interface OrderActivity {
void validateOrder(String orderId);
void processPayment(String orderId);
void shipOrder(String orderId);
void sendConfirmation(String orderId);
void refundPayment(String orderId);
void cancelShipment(String orderId);
void sendCancellationNotification(String orderId, String reason);
void logOrderEvent(String orderId, String event, OrderStatus status);
void sendAlert(String orderId, AlertLevel level, String message);
}实现 OrderActivity
import lombok.extern.log4j.Log4j2;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import me.vrnsky.temporalspringboot.model.AlertLevel;
import me.vrnsky.temporalspringboot.model.OrderStatus;
@Log4j2
public class OrderActivityImpl implements OrderActivity {
@Override
public void validateOrder(String orderId) {
log.info("Validating order {}", orderId);
}
@Override
public void processPayment(String orderId) {
log.info("Processing payment {}", orderId);
}
@Override
public void shipOrder(String orderId) {
log.info("Shipping order {}", orderId);
}
@Override
public void sendConfirmation(String orderId) {
log.info("Sending confirmation {}", orderId);
}
@Override
public void refundPayment(String orderId) {
log.info("Refunding payment {}", orderId);
}
@Override
public void cancelShipment(String orderId) {
log.info("Cancelling shipment {}", orderId);
}
@Override
public void sendCancellationNotification(String orderId, String reason) {
log.info("Cancelling notification {}", orderId);
}
@Override
public void logOrderEvent(String orderId, String event, OrderStatus status) {
log.info("Order {} event {}", orderId, event);
}
@Override
public void sendAlert(String orderId, AlertLevel level, String message) {
log.info("Sending alert {}", orderId);
}
}现在,让我们使用补偿逻辑和监控来构建增强的工作流程。
import io.temporal.activity.ActivityOptions;
import io.temporal.common.RetryOptions;
import io.temporal.workflow.Workflow;
import me.vrnsky.temporalspringboot.activity.OrderActivity;
import me.vrnsky.temporalspringboot.model.AlertLevel;
import me.vrnsky.temporalspringboot.model.OrderResult;
import me.vrnsky.temporalspringboot.model.OrderStatus;
import java.time.Duration;
public class OrderProcessWorkflowImpl implements OrderProcessingWorkflow {
private OrderStatus currentStatus = OrderStatus.CREATED;
private boolean paymentProcessed = false;
private boolean shipmentCreated = false;
private final ActivityOptions options = ActivityOptions.newBuilder()
.setScheduleToCloseTimeout(Duration.ofMinutes(5))
.setRetryOptions(RetryOptions.newBuilder()
.setMaximumAttempts(3)
.setInitialInterval(Duration.ofSeconds(1))
.setMaximumInterval(Duration.ofSeconds(10))
.build())
.build();
private final OrderActivity orderActivity = Workflow.newActivityStub(OrderActivity.class, options);
@Override
public OrderResult processOrder(String orderId) {
try {
try {
orderActivity.validateOrder(orderId);
currentStatus = OrderStatus.VALIDATED;
orderActivity.logOrderEvent(orderId, "Order validated", currentStatus);
} catch (Exception e) {
handleFailure(orderId, "Order validation failed", e);
return new OrderResult(orderId, currentStatus, "Validation failed: " + e.getMessage());
}
// Process Payment
try {
orderActivity.processPayment(orderId);
paymentProcessed = true;
currentStatus = OrderStatus.PAYMENT_PROCESSED;
orderActivity.logOrderEvent(orderId, "Payment processed", currentStatus);
} catch (Exception e) {
handleFailure(orderId, "Payment processing failed", e);
return new OrderResult(orderId, currentStatus, "Payment failed: " + e.getMessage());
}
// Ship Order
try {
orderActivity.shipOrder(orderId);
shipmentCreated = true;
currentStatus = OrderStatus.SHIPPED;
orderActivity.logOrderEvent(orderId, "Order shipped", currentStatus);
} catch (Exception e) {
handleFailure(orderId, "Shipping failed", e);
return new OrderResult(orderId, currentStatus, "Shipping failed: " + e.getMessage());
}
// Send Confirmation
try {
orderActivity.sendConfirmation(orderId);
currentStatus = OrderStatus.COMPLETED;
orderActivity.logOrderEvent(orderId, "Order completed", currentStatus);
return new OrderResult(orderId, currentStatus, "Order completed successfully");
} catch (Exception e) {
handleFailure(orderId, "Confirmation failed", e);
return new OrderResult(orderId, currentStatus, "Confirmation failed: " + e.getMessage());
}
} catch (Exception e) {
handleFailure(orderId, "Unexpected error", e);
return new OrderResult(orderId, currentStatus, "Unexpected error: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
@Override
public OrderStatus getOrderStatus() {
return currentStatus;
}
@Override
public void cancelOrder(String reason) {
if (currentStatus == OrderStatus.COMPLETED || currentStatus == OrderStatus.CANCELLED) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot cancel completed or already cancelled order");
}
compensate(Workflow.getInfo().getWorkflowId(), reason);
}
private void handleFailure(String orderId, String message, Exception e) {
currentStatus = OrderStatus.COMPENSATING;
orderActivity.logOrderEvent(orderId, message, currentStatus);
orderActivity.sendAlert(orderId, AlertLevel.ERROR, message + ":" + e.getMessage());
}
private void compensate(String orderId, String reason) {
try {
if (shipmentCreated) {
orderActivity.cancelShipment(orderId);
orderActivity.logOrderEvent(orderId, "Shipment cancelled", currentStatus);
}
if (paymentProcessed) {
orderActivity.refundPayment(orderId);
orderActivity.logOrderEvent(orderId, "Payment refunded", currentStatus);
}
orderActivity.sendCancellationNotification(orderId, reason);
currentStatus = OrderStatus.CANCELLED;
orderActivity.logOrderEvent(orderId, "Order cancelled", currentStatus);
} catch (Exception e) {
currentStatus = OrderStatus.FAILED;
orderActivity.sendAlert(orderId, AlertLevel.CRITICAL, "Compensation failed: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
}总结
Spring Boot 和 Temporal 为构建复杂分布式应用程序提供了强大的基础支持。我们构建的示例展示了其主要优势:
- 自动重试机制和状态持久性
- 平滑的管理故障和补偿逻辑
- 工作流和活动之间有明确的分离
在执行复杂的业务流程时,请谨慎选择工具。Temporal 的工作流编排增强了 Spring Boot 的依赖注入和配置功能。这使得开发人员能够专注于业务逻辑,而 Temporal 则负责处理分布式系统的可靠性问题。





没有回复内容