在应用程序测试中,全面的自动化对于确保云原生应用程序的可靠性和最佳性能至关重要,特别是在采用持续部署以优先考虑快速上线策略时。
在最近于班加罗尔举行的测试自动化研讨会上,我进行了一项民意调查,以深入了解有关测试自动化的企业技术前景。结果非常明显:虽然采用微服务架构的势头强劲,但大多数组织要达到 DORA 标准定义的精英团队地位,还有很长的路要走。
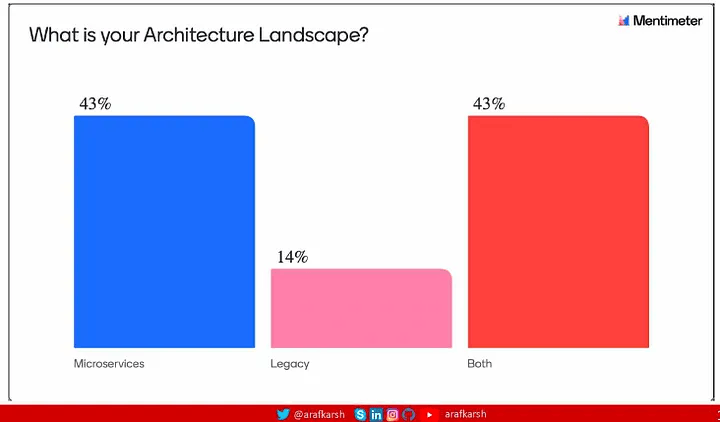
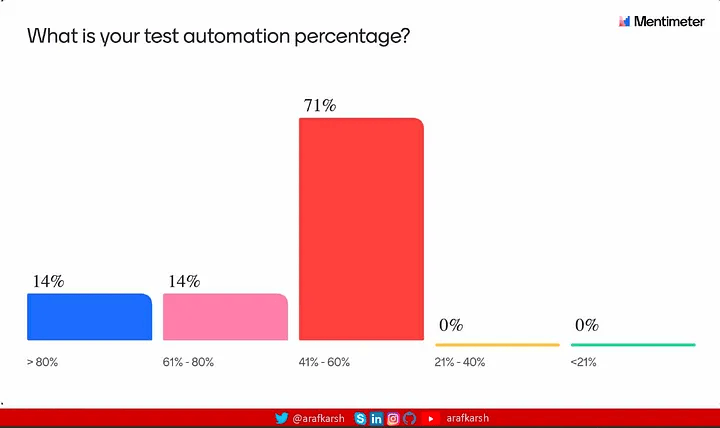
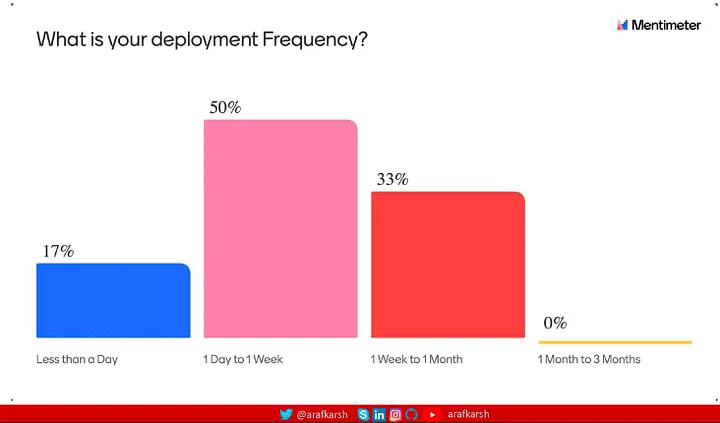
我建议您浏览 Google 的 2024 年 DORA 报告以获得更深入的见解。本系列将重点介绍帮助团队过渡到 Elite 身份的可行策略,特别强调推进考试自动化实践。
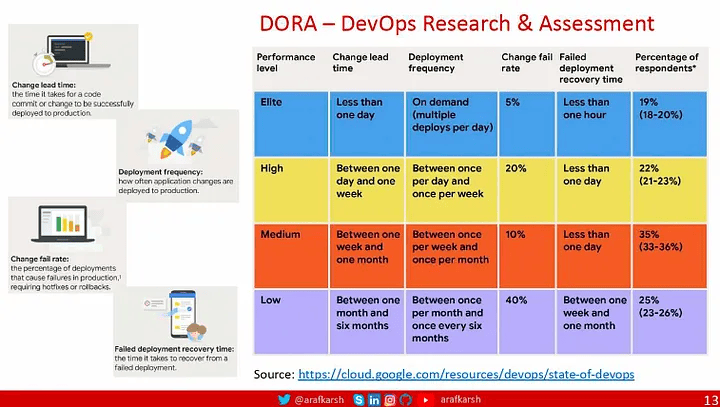
在本系列的第二部分中,我们将深入研究根据 DORA 标准定义精英团队的特征。现在,让我们探索为云原生架构(通常称为微服务架构)量身定制的测试自动化策略。
一旦我们确定了测试自动化的关键重点领域,我们将深入研究目前市场上可用的 AI 驱动的测试自动化工具
云原生(微服务)测试自动化策略
该方法包括单元测试、集成测试、合同测试和端到端测试。
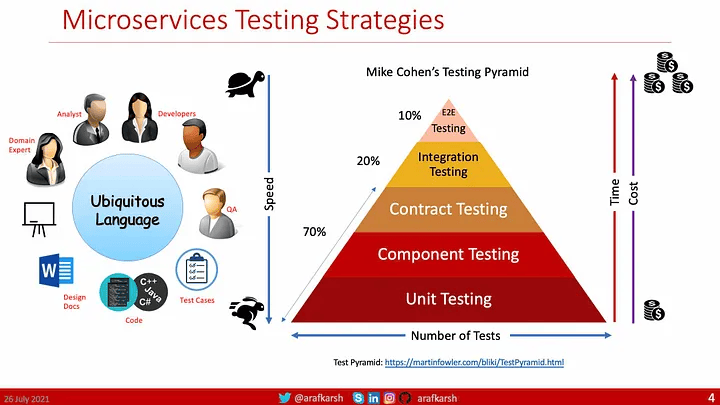
来源:Slidedeck:微服务架构系列 — 测试策略
- 单元测试:单元测试对应用程序中最小的可测试软件进行测试,以确定它是否按预期运行。
- 组件测试:组件测试将执行软件的范围限制在被测系统的一部分,通过内部代码接口操纵系统,并使用测试替身将被测代码与其他组件隔离开来。
- 由 Pact 等工具提供的合约测试可确保服务符合商定的 API 合约。
- 集成测试:集成合同测试是在外部服务的边界进行的测试,用于验证它是否满足使用服务所期望的合同。
- 端到端测试:端到端测试验证系统是否满足外部要求并实现其目标,端到端测试整个系统。
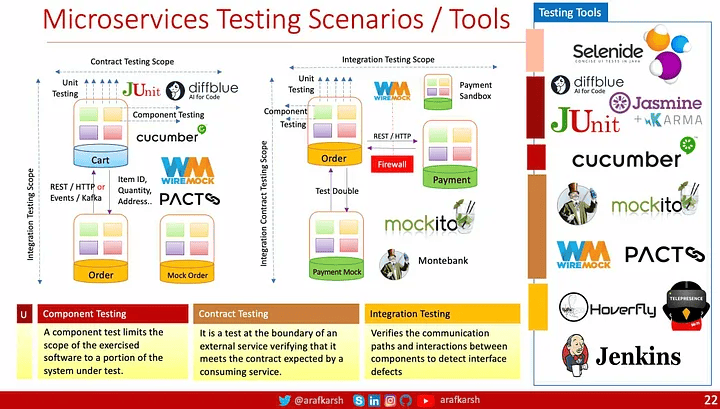
GitHub 存储库:微服务测试快速入门
此外,用于容器编排的 Kubernetes 和用于服务网格的 Istio 等工具可以帮助创建真实的测试环境,使测试过程更加健壮和可靠。
在深入研究测试自动化的细节之前,必须首先探索更广泛的软件开发。这将有助于我们了解自动化在流程中的位置以及可用的各种自动化类型。
下图说明了软件开发生命周期 (SDLC) 中的 SpecOps 工作流程,强调了从规范 (Specs) 到运营 (Ops) 的过程。
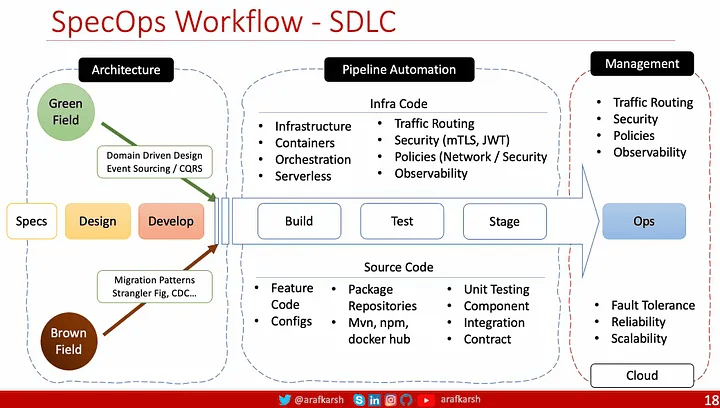
来源:Slidedeck:微服务架构系列 — 测试策略
设计和开发规格
Green Field Projects:
- 这些操作涉及从头开始构建应用程序。重点:
- 领域驱动设计 (DDD):围绕核心业务领域构建项目。
- 事件溯源/CQRS:分别处理状态更改和查询职责。
Brown Field Projects:
涉及对现有系统进行现代化改造或增强。技术包括:
迁移模式:像 Strangler Fig 模式这样的策略,用于一步一步地逐步替换遗留系统。
变更数据捕获 (CDC):实时捕获数据更改以实现无缝迁移。
管道自动化(构建→测试→阶段)
该部分自动执行各个 SDLC 阶段,以确保效率和可靠性。
- 构建 :专注于编译、打包和准备用于部署的源代码。包括:
- 源代码:使用 Maven、NPM 和 Docker Hub 等工具进行功能代码、配置和依赖项管理。
2. 测试自动化:
通过多个测试层确保质量和性能:
- 单元测试:验证各个组件。
- 组件测试:测试应用程序的隔离部分。
- 契约测试:验证微服务之间的 API 契约。
- 集成测试:确保组件协同工作。
3. 基础设施自动化(基础设施即代码):
自动化基础设施配置和管理,包括:
- 容器(例如 Docker)。
- 编排(例如 Kubernetes)。
- 用于可扩展且经济高效的解决方案的无服务器架构。
服务网格(例如 Istio):用于可观察性、安全性和流量路由
- 流量路由:有效管理和引导应用程序流量。
- 安全性:实施 mTLS(双向 TLS)以实现安全通信,并使用 JWT(JSON Web 令牌)进行身份验证。
- 策略:必须应用网络和安全策略来保持合规性并拥有强大的纵深防御安全架构。
4.阶段:
准备应用程序以在类似生产的环境中部署。
运维(Ops)
一旦部署应用程序,重点就转移到操作可靠性上。
- 可观察性:使用日志、指标和跟踪监控性能并识别问题。
最终目标
- 容错:确保系统可以从故障中恢复。
- 可靠性:在不同条件下提供一致的性能。
- 可扩展性:无缝扩展以满足需求波动
此工作流程突出了持续集成和部署 (CI/CD) 管道,并高度重视自动化。
它将架构原则与开发、测试和操作实践联系起来,在云原生环境中提供可扩展、可靠和可维护的软件。
AI 驱动的顶级测试自动化工具
让我们重新关注测试自动化,特别是探索人工智能驱动的测试自动化以及这些工具如何增强测试过程。以下是此类工具的一些示例。
1. Diffblue Cover
目的:自动生成Java应用程序的单元测试。
主要特点:
- 由人工智能驱动的测试创建可实现高代码覆盖率。
- 支持 JUnit 和 TestNG。
- 与 IntelliJ IDEA 和 Maven 集成。
使用案例:自动生成 Spring Boot 服务、控制器和存储库的单元测试。
2. Testim
目的:用于创建、执行和维护自动化功能测试的人工智能驱动工具。
主要特点:
- 自愈测试能力,适应UI变化。
- 与 CI/CD 管道集成。
- 对微服务的 API 测试支持。
使用案例:使用动态用户界面对 Spring Boot 应用程序进行功能和端到端测试。
3. Mabl
目的:基于云、人工智能驱动的功能测试自动化测试。
主要特点:
- 支持 REST API 测试,非常适合 Spring Boot 微服务。
- 人工智能驱动的缺陷检测。
- 与 CI/CD 工作流程无缝集成。
使用案例:Spring Boot 应用程序中微服务和 API 层的综合测试。
4. Katalon Studio
目的:一个多功能测试平台,具有用于 Web、API 和移动测试的 AI 增强功能。
主要特点:
- 支持使用 Groovy 编写基于 Java 的测试脚本。
- 人工智能驱动的物体检测和智能测试建议。
- 内置 API 测试功能。
使用案例:在 Spring Boot 应用程序中自动化 RESTful API 测试。
5. Functionize
目的:用于功能和性能测试的人工智能驱动平台。
主要特点:
- 用于创建测试用例的自然语言处理。
- 人工智能驱动的测试执行和维护。
- 与 Jenkins 和 GitLab 等 CI/CD 工具集成。
使用案例:Spring Boot 应用程序中用户界面和 API 的功能测试。
6. Applitools
目的:人工智能驱动的视觉测试平台。
主要特点:
- 通过无缝 SDK 集成支持 Java 和 Spring Boot 应用程序。
- 用于检测跨环境的 UI 变化的视觉 AI。
- 与 Selenium、Cypress 和 TestNG 集成。
使用案例:验证 Spring Boot Web 应用程序中前端组件的视觉一致性。
7. Tricentis Tosca
目的:人工智能驱动的持续测试平台。
主要特点:
- 支持 Java 应用程序的 API 和 UI 测试。
- 自愈测试和智能测试优化。
- 与 CI/CD 管道集成。
使用案例:Spring Boot 应用程序的端到端测试,包括 REST API 和前端组件。
8. Selenium with AI Add-ons (Healenium)
目的:利用 AI 功能增强 Selenium 测试。
主要特点:
- Healenium:用于解决损坏的定位器的自愈测试。
使用案例:使用动态界面对 Spring Boot 应用程序进行自动化 Web UI 测试。
9. SmartBear TestComplete
目的:用于功能和回归测试的人工智能增强测试自动化。
主要特点:
- 支持具有脚本和记录回放功能的 Java 应用程序。
- AI 驱动的 UI 元素对象识别。
- 与 Jenkins 和 Git 集成。
用例:Spring Boot 前端和后端组件的功能测试。
10. ReTest
目的:人工智能驱动的回归测试工具。
主要特点:
- 利用 AI 进行智能测试维护。
- 支持基于 Java 的应用程序。
- 自动检测应用程序中的更改。
使用案例:对不断发展的 Spring Boot 应用程序进行回归测试。
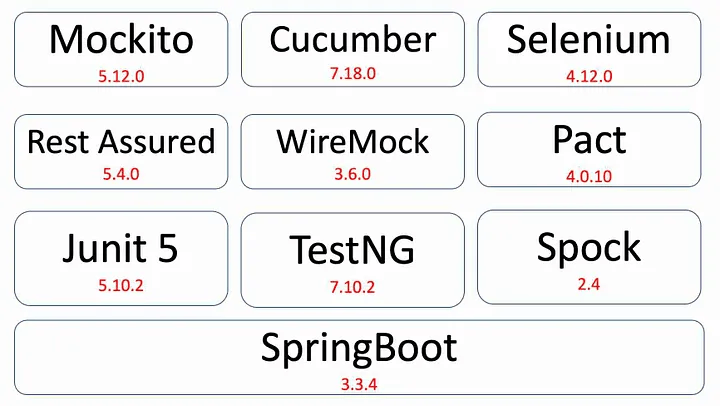
GitHub Repository — Java 23, SpringBoot 3.3.4 测试案例
在深入研究 DiffBlue 之前,让我概述 GitHub 存储库,并展示跨各种平台和测试自动化库的示例测试用例。
下图突出显示了这些工具以及每个工具或库可用的相应测试用例数。
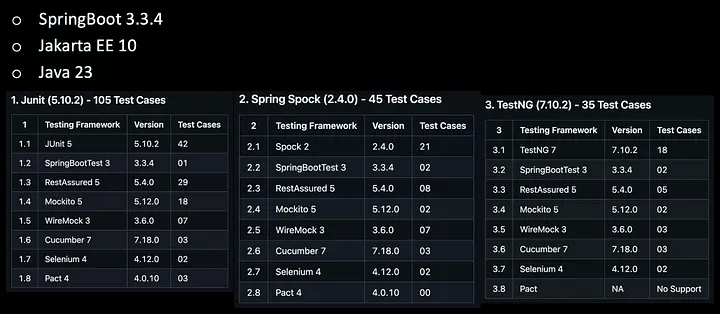
GitHub 存储库:微服务测试快速入门
Dependencies
- Java 21+
- SpringBoot 3.3.4
- Jakarta EE 10
Test Platforms
- JUnit 5 (5.10.2)
- TestNG 7 (7.10.2)
- Spring Spock 2 (2.4.0)
Test Suites
- Mockito (5.12.0)
- Cucumber (7.18.0)
- Selenium (4.12.0)
- Rest Assured (5.4.0)
- WireMock (3.6.0)
- Pact (4.0.10)
pom.xml
<!-- Testing Platforms ============================================= -->
<junit.jupiter.version>5.10.2</junit.jupiter.version>
<testng.version>7.10.2</testng.version>
<spock.version>2.4-M1-groovy-4.0</spock.version>
<!-- Testing Frameworks =========================================== -->
<hamcrest.version>2.2</hamcrest.version>
<truth.version>1.0.1</truth.version>
<mockito.version>5.12.0</mockito.version>
<wiremock.version>3.6.0</wiremock.version>
<cucumber.version>7.18.0</cucumber.version>
<selenium.version>4.12.0</selenium.version>
<restassured.version>5.4.0</restassured.version>
<pact.version>4.0.10</pact.version>
<assertj.version>3.26.3</assertj.version>
<!-- Showing only relevant code -->
<!-- Showing only relevant code -->
<!-- ================================================================= -->
<!--
1. You should place rest-assured before the JUnit dependency declaration in your pom.xml / build.gradle
in order to make sure that the correct version of Hamcrest is used.
2. REST Assured includes JsonPath and XmlPath as transitive dependencies
-->
<!-- ================================================================= -->
<!-- REST Assured Framework -->
<!-- ================================================================= -->
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/io.rest-assured/rest-assured -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.rest-assured</groupId>
<artifactId>rest-assured</artifactId>
<version>${restassured.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.scribejava</groupId>
<artifactId>scribejava-apis</artifactId>
<version>8.3.3</version>
</dependency>
<!-- UNIT TESTING ==================================================== -->
<!-- ================================================================= -->
<!-- JUnit 5 Framework -->
<!-- ================================================================= -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-jupiter</artifactId>
<!-- Version defined in the Properties -->
<version>${junit.jupiter.version}</version>
<!-- Junit Dependencies are ONLY Part of test Scope it won't be there in your build. -->
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.junit.jupiter/junit-jupiter-api -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-jupiter-api</artifactId>
<version>${junit.jupiter.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.junit.jupiter/junit-jupiter-engine -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-jupiter-engine</artifactId>
<version>${junit.jupiter.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.vintage</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-vintage-engine</artifactId>
<version>${junit.jupiter.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-jupiter-migrationsupport</artifactId>
<version>${junit.jupiter.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-jupiter-params</artifactId>
<version>${junit.jupiter.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- JUnit External Modules -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hamcrest</groupId>
<artifactId>hamcrest-core</artifactId>
<version>${hamcrest.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.google.truth</groupId>
<artifactId>truth</artifactId>
<version>${truth.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.assertj/assertj-core -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.assertj</groupId>
<artifactId>assertj-core</artifactId>
<version>${assertj.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- COMPONENT / CONTRACT TESTING ==================================== -->
<!-- ================================================================= -->
<!-- Cucumber Framework -->
<!-- ================================================================= -->
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/io.cucumber/cucumber-java -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.cucumber</groupId>
<artifactId>cucumber-java</artifactId>
<version>${cucumber.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/io.cucumber/cucumber-junit -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.cucumber</groupId>
<artifactId>cucumber-junit</artifactId>
<version>${cucumber.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/io.cucumber/cucumber-core -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.cucumber</groupId>
<artifactId>cucumber-core</artifactId>
<version>${cucumber.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/io.cucumber/cucumber-java8 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.cucumber</groupId>
<artifactId>cucumber-java8</artifactId>
<version>${cucumber.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.cucumber</groupId>
<artifactId>cucumber-junit-platform-engine</artifactId>
<version>${cucumber.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/io.cucumber/cucumber-picocontainer -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.cucumber</groupId>
<artifactId>cucumber-picocontainer</artifactId>
<version>${cucumber.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.cucumber</groupId>
<artifactId>cucumber-testng</artifactId>
<version>${cucumber.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- ================================================================= -->
<!-- Selenium Framework -->
<!-- ================================================================= -->
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.seleniumhq.selenium/selenium-java -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.seleniumhq.selenium</groupId>
<artifactId>selenium-java</artifactId>
<version>${selenium.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.seleniumhq.selenium/selenium-api -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.seleniumhq.selenium</groupId>
<artifactId>selenium-api</artifactId>
<version>${selenium.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.seleniumhq.selenium/selenium-support -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.seleniumhq.selenium</groupId>
<artifactId>selenium-support</artifactId>
<version>${selenium.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- ================================================================= -->
<!-- Mockito Framework -->
<!-- ================================================================= -->
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.mockito/mockito-core -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mockito</groupId>
<artifactId>mockito-core</artifactId>
<version>${mockito.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.mockito/mockito-junit-jupiter -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mockito</groupId>
<artifactId>mockito-junit-jupiter</artifactId>
<version>${mockito.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- ================================================================= -->
<!-- INTEGRATION / CONTRACT TESTING ================================== -->
<!-- ================================================================= -->
<!-- ================================================================= -->
<!-- Spring Boot Testing Framework -->
<!-- ================================================================= -->
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework.boot/spring-boot-starter-test -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<version>${spring.boot.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
<!-- Exclude JUnit as Spring Boot Starter Test uses JUnit 4 -->
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<!-- ================================================================= -->
<!-- WireMock Framework -->
<!-- ================================================================= -->
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.wiremock/wiremock -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.wiremock</groupId>
<artifactId>wiremock</artifactId>
<version>${wiremock.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- ================================================================= -->
<!-- Pact Framework -->
<!-- ================================================================= -->
<dependency>
<groupId>au.com.dius</groupId>
<artifactId>pact-jvm-provider-junit5</artifactId>
<version>${pact.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>au.com.dius</groupId>
<artifactId>pact-jvm-consumer-junit5</artifactId>
<version>${pact.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/au.com.dius/pact-jvm-provider -->
<dependency>
<groupId>au.com.dius</groupId>
<artifactId>pact-jvm-provider</artifactId>
<version>${pact.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/au.com.dius/pact-jvm-consumer-junit -->
<dependency>
<groupId>au.com.dius</groupId>
<artifactId>pact-jvm-consumer-junit</artifactId>
<version>${pact.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/au.com.dius/pact-jvm-consumer -->
<dependency>
<groupId>au.com.dius</groupId>
<artifactId>pact-jvm-consumer</artifactId>
<version>${pact.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Showing only relevant code -->Diffblue Cover
Diffblue Cover 是一种 AI 驱动的工具,旨在为 Java 应用程序(包括使用 Spring Boot 框架构建的应用程序)自动生成单元测试。通过利用强化学习,它可以生成可靠、可维护的单元测试,这些测试可以正确编译和运行,从而有助于提高代码质量并加快开发周期。

Diffblue Cover 的主要特点:
- 自主测试生成:Diffblue Cover 自动为 Java 代码编写全面的单元测试,从而有效减少创建测试时通常需要的手动工作。
- 与开发环境集成:它为 IntelliJ IDEA 提供了一个插件,使开发人员能够直接在其集成开发环境 (IDE) 中生成单元测试。这种集成简化了测试过程,允许在编写或修改代码时立即创建测试。
- 对 Spring Boot 应用程序的支持:Diffblue Cover 与 Spring Boot 应用程序兼容,能够为控制器和服务等各种组件生成单元测试。它利用 Mockito 等模拟框架来处理依赖项,确保测试被隔离并专注于被测单元。
- 提高开发人员的工作效率:通过自动生成单元测试,Diffblue Cover 使开发人员能够将更多精力放在编写应用程序代码上,从而提高整体生产力并更快地交付高质量软件
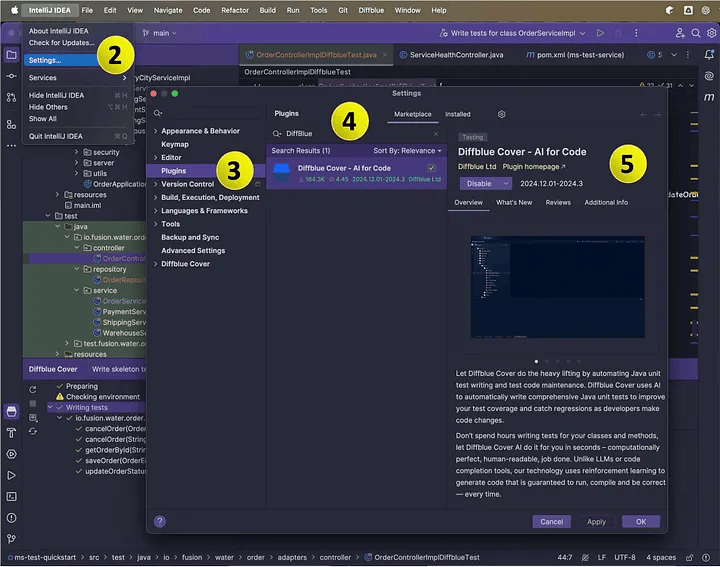
为 IntelliJ IDE 设置 Diffblue Cover
- 打开 IntelliJ IDEA
- 导航到 Settings → File 菜单(或 macOS 上的 IntelliJ IDEA → Settings)。
- 在设置窗口中,从左侧菜单中选择 Plugins。
- 在 Marketplace 选项卡中,搜索 Diffblue Cover。
- 重新启动 IntelliJ IDEA 以完成安装。
自动生成测试用例
Order Service
@Service
public class OrderServiceImpl implements OrderService {
@Autowired
private OrderRepository orderRepo;
@Autowired
private PaymentService paymentService;
/**
* For Auto wiring the service with Order Repo and Payment Service
* @param _orderRepo
* @param _paymentService
*/
public OrderServiceImpl(OrderRepository _orderRepo, PaymentService _paymentService) {
orderRepo = _orderRepo;
paymentService = _paymentService;
}
// THIS IS ONLY TO DO THE DEMO OF PACT
@Autowired
private ExternalGateWay externalGateWay;
@Override
public OrderEntity getOrderById(String _id) {
// return orderRepo.getOrderById(_id);
return mockGetOrderById(_id);
}
/**
* This is Only for PACT DEMO
* @param _order
* @return
*/
public OrderEntity saveOrderExternal(OrderEntity _order) {
return externalGateWay.saveOrder(_order);
}
@Override
public OrderEntity processOrder(OrderEntity _order) {
// Save order
OrderEntity order = orderRepo.saveOrder(_order);
if(order != null) {
// Make Payments
PaymentStatus payStatus = paymentService.processPayments(
order.getPaymentDetails());
// Update Payment Status
order.setPaymentStatus(payStatus);
}
return order;
}
// ...
/**
* Update Order Status
*/
public OrderEntity updateOrderStatus(String _id, String _status) {
// Fetch Order based on Order Id
// OrderEntity order = orderRepo.getOrderById(_id);
OrderEntity order = mockGetOrderById(_id);
// Check Order Status and set the the status in the Order
if(_status.equalsIgnoreCase(OrderStatus.READY_FOR_SHIPMENT.name())) {
order.orderReadyForShipment();
} else if (_status.equalsIgnoreCase(OrderStatus.PAYMENT_EXPECTED.name())) {
order.orderWaitingForPayment();
}
return orderRepo.saveOrder(order);
}
/**
* Adding a New Method to test DiffBlue Cover
* Ship Order
* @param _id
* @return
*/
public OrderEntity shipOrder(String _id) {
// Fetch Order based on Order Id
OrderEntity order = mockGetOrderById(_id);
order.orderReadyForShipment();
return order;
}
@Override
public PaymentStatus processPayments(PaymentDetails _paymentDetails) {
return paymentService.processPayments(_paymentDetails);
}
// ... Showing only relevant code ...
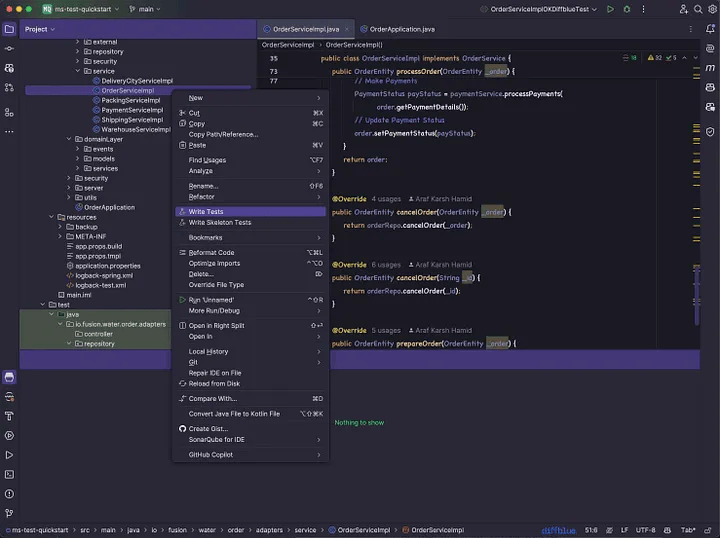
}右键单击 Code (Controller / Service) 以生成测试用例
3. 测试用例生成正在进行中
生成测试用例
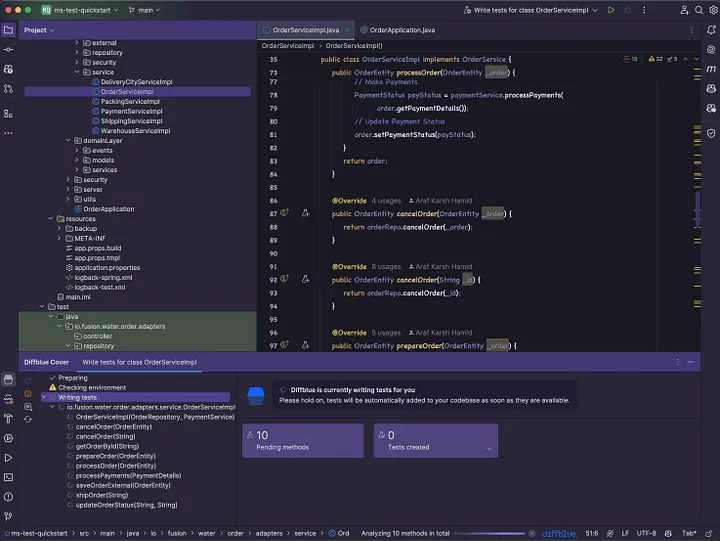
正在进行测试生成
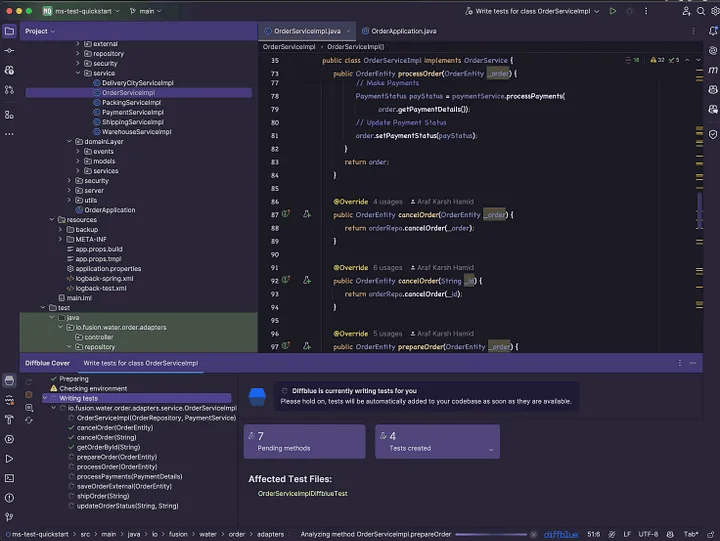
正在进行测试生成
4. 测试用例生成完成
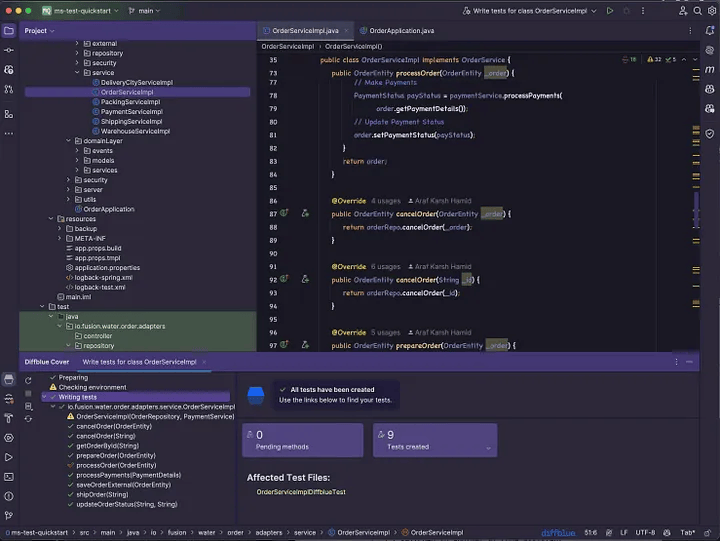
测试生成已完成
5. 测试自动生成的 Order Service 测试代码
Diffblue Cover 主要是一个单元测试生成工具,它通常依赖于 Mockito(或类似的模拟框架)来隔离依赖项。
以下是 Diffblue 生成的 OrderService 自动生成的代码。虽然它可能并不完全完美,但它提供了一个坚实的起点,让您可以快速建立基础。您可以通过添加任何缺失的部分来完成功能,从而轻松增强生成的代码。这种方法显著减少了编写测试用例所需的时间。
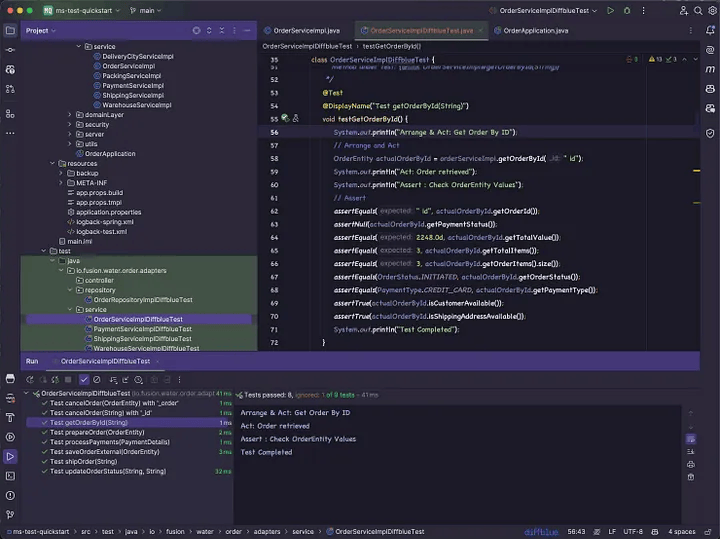
自动生成的测试用例
@ContextConfiguration(classes = {OrderServiceImpl.class})
@ExtendWith(SpringExtension.class)
@DisabledInAotMode
class OrderServiceImplDiffblueTest {
@MockBean
private ExternalGateWay externalGateWay;
@MockBean
private OrderRepository orderRepository;
@Autowired
private OrderServiceImpl orderServiceImpl;
@MockBean
private PaymentService paymentService;
/**
* Test {@link OrderServiceImpl#getOrderById(String)}.
* <p>
* Method under test: {@link OrderServiceImpl#getOrderById(String)}
*/
@Test
@DisplayName("Test getOrderById(String)")
void testGetOrderById() {
System.out.println("Arrange & Act: Get Order By ID");
// Arrange and Act
OrderEntity actualOrderById = orderServiceImpl.getOrderById(" id");
System.out.println("Act: Order retrieved");
System.out.println("Assert : Check OrderEntity Values");
// Assert
assertEquals(" id", actualOrderById.getOrderId());
assertNull(actualOrderById.getPaymentStatus());
assertEquals(2248.0d, actualOrderById.getTotalValue());
assertEquals(3, actualOrderById.getTotalItems());
assertEquals(3, actualOrderById.getOrderItems().size());
assertEquals(OrderStatus.INITIATED, actualOrderById.getOrderStatus());
assertEquals(PaymentType.CREDIT_CARD, actualOrderById.getPaymentType());
assertTrue(actualOrderById.isCustomerAvailable());
assertTrue(actualOrderById.isShippingAddressAvailable());
System.out.println("Test Completed");
}
// ... Showing only relevant code ...
}当我尝试为 REST 控制器生成代码时,结果远非令人满意。然而,对于存储库和服务,Diffblue 表现非常出色,生成了一个包含所有关键元素的功能性代码库。只需额外花费 20-30% 的时间来优化和完成测试用例,您就可以有效地实现全面覆盖。





没有回复内容