在当今快节奏的软件开发世界中,弹性是应用程序的关键特性之一。网络问题、数据库宕机或第三方服务故障是常见的场景,可能导致临时中断。与其让这些故障导致应用程序崩溃,不如通过实现重试机制使系统能够优雅地恢复。
Spring Boot 提供了使用 spring-retry 模块实现重试的强大方式。本文将探讨如何在 Spring Boot 中使用 Spring Retry,涵盖其配置、实现以及构建弹性应用程序的最佳实践。
什么是 Spring Retry?
Spring Retry 是一个为 Spring 应用程序提供重试操作支持的库。它使开发人员能够通过重试失败的操作来处理临时问题,而不是直接放弃。这种机制可以用于以下场景:
- • 重试对第三方服务的失败 API 调用。
- • 在临时问题发生时重试数据库事务。
- • 实现指数退避以避免资源过载。
该库与 Spring Boot 无缝集成,使得通过最少的配置即可轻松为应用程序添加重试逻辑。
Spring Retry 的关键特性
1. 重试策略:自定义重试行为,包括重试次数、重试的异常类型以及退避策略。
2. 退避策略:实现固定或指数延迟,避免对外部系统造成过大压力。
3. 注解集成:使用 @Retryable 和 @Recover 等注解进行声明式重试处理。
4. 有状态和无状态重试:选择有状态重试(跟踪调用状态)或无状态重试(每次尝试独立处理)。
为什么使用重试机制?
重试机制增强了应用程序的弹性和可靠性。它们允许您:
1. 处理临时故障:重试由于临时问题(如网络延迟或服务不可用)而失败的操作。
2. 改善用户体验:通过自动缓解故障,确保最终用户的交互更加顺畅。
3. 减少人工干预:自动化恢复过程,最大限度地减少停机时间并减少人工干预的需求。
4. 实现断路器模式:将重试与断路器结合使用,防止过载故障系统。
在 Spring Boot 中设置 Spring Retry
步骤 1:添加 Spring Retry 依赖
要开始使用 Spring Retry,请在 pom.xml 文件中添加以下依赖项:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.retry</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-retry</artifactId>
<version>2.0.10</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId>
</dependency>spring-retry 依赖项启用了重试机制,而 spring-boot-starter-aop 依赖项允许您使用注解进行声明式重试。
步骤 2:启用 Spring Retry
在 Spring Boot 应用程序中,通过在配置类中添加 @EnableRetry 注解来启用重试:
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.retry.annotation.EnableRetry;
@Configuration
@EnableRetry
public class AppConfig {
}使用 @Retryable 和 @Recover 注解
@Retryable
@Retryable 注解用于标记需要重试操作的方法。您可以配置以下参数:
- •
maxAttempts:最大重试次数。 - •
retryFor:指定需要重试的异常类型。 - •
exclude:指定不需要重试的异常类型。 - •
backoff:定义延迟或退避策略。
import org.springframework.retry.annotation.Retryable;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
@Slf4j
public class ApiService {
@Retryable(
retryFor = {RuntimeException.class},
maxAttempts = 3,
backoff = @Backoff(delay = 2000, multiplier = 2)
)
public String fetchData() {
log.info("Attempting to fetch data...");
if (Math.random() > 0.5) {
throw new RuntimeException("Temporary API failure");
}
return "Data retrieved successfully";
}
}在此示例中:
- • 如果发生
RuntimeException,fetchData方法将最多重试 3 次。 - • 每次重试之间有 2 秒的初始延迟,后续每次重试的延迟时间加倍(指数退避)。
@Service
@Slf4j
public class RetryService {
private int attemptCount = 0;
@Retryable(
retryFor = {RuntimeException.class},
maxAttempts = 3,
backoff = @Backoff(delay = 2000, multiplier = 2)
)
public String callExternalService(){
attemptCount++;
log.info("Attempting to call external service. Attempt #" + attemptCount);
// 模拟一个在前两次调用时失败的服务
if (attemptCount < 3) {
log.info("Service temporarily unavailable");
throw new RuntimeException("Service temporarily unavailable");
}
return "Service call successful!";
}
}在此示例中:
- • 如果发生
RuntimeException,callExternalService方法将最多重试 3 次。 - • 每次重试之间有 2 秒的初始延迟,后续每次重试的延迟时间加倍(指数退避)。
@Recover
@Recover 注解提供了一个在所有重试尝试失败后调用的回退方法。回退方法必须具有相同的返回类型,并将异常作为第一个参数。
示例:
import org.springframework.retry.annotation.Recover;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
@Slf4j
public class RetryService {
@Retryable(retryFor = {RuntimeException.class}, maxAttempts = 3)
public String fetchData() {
log.info("Attempting to fetch data...");
throw new RuntimeException("API failure");
}
@Recover
public String recover(RuntimeException e) {
log.info("Recovering from failure: " + e.getMessage());
return "Default data";
}
}在此示例中:
- • 如果所有重试尝试都失败,将调用
recover方法以提供回退响应。
REST API 示例
演示调用重试服务的不同场景。
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/v1")
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class RetryController {
private final RetryService retryService;
@GetMapping("/simple-retry")
public ResponseEntity<ApiResponse> simpleRetry() {
try {
String result = retryService.callExternalService();
return ResponseEntity.ok(new ApiResponse(true, result, null));
} catch (Exception e) {
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR)
.body(new ApiResponse(false, null, e.getMessage()));
}
}
@GetMapping("/simple-recovery")
public ResponseEntity<ApiResponse> simpleRecovery() {
try {
String result = retryService.fetchData();
return ResponseEntity.ok(new ApiResponse(true, result, null));
} catch (Exception e) {
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR)
.body(new ApiResponse(false, null, e.getMessage()));
}
}
}- 简单重试(
GET /api/v1/simple-retry):
- 基本重试功能
- 固定重试次数
- 指数退避
- 带恢复的重试(
GET /api/v1/simple-recovery):
- 基本恢复功能
- 可强制错误以进行测试
- 自定义恢复方法以返回响应
测试 Spring Boot 重试注解
使用 Postman 测试 Spring Boot 应用程序中的 @Retryable 注解。
- 1. 测试发送请求到
GET /api/v1/simple-retry
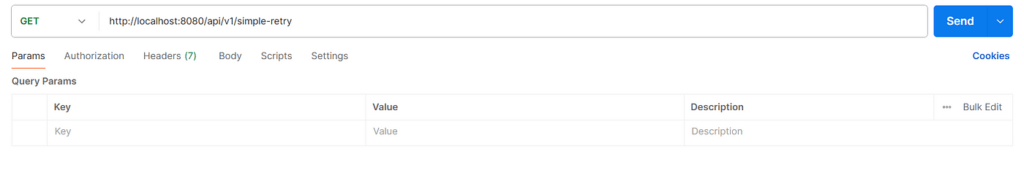
请求日志:
Attempting to call external service. Attempt #1
Service temporarily unavailable
Attempting to call external service. Attempt #2
Service temporarily unavailable
Attempting to call external service. Attempt #3

测试结果:当客户端向服务器发送请求时,服务器在前两次调用中抛出 RuntimeException,然后成功返回响应。测试结果符合预期。
2. 测试发送请求到 GET /api/v1/simple-recovery
请求日志:
Attempting to fetch data...
Attempting to fetch data...
Attempting to fetch data...
Recovering from failure: API failure
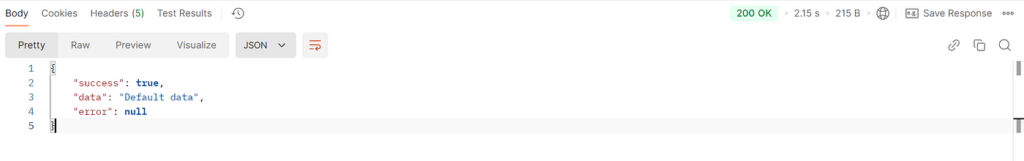
测试结果:当客户端向服务器发送请求时,服务器在前三次调用中抛出 RuntimeException,然后进入恢复方法并返回 Default data 消息。测试结果符合预期。
有状态与无状态重试
Spring Retry 支持两种类型的重试:
- 无状态重试:默认行为,每次重试独立处理。适用于幂等操作。
- 有状态重试:在重试之间保留状态,适用于非幂等操作(如数据库事务)。
通过在 @Retryable 中将 stateful 属性设置为 true 来启用有状态重试。
示例:
@Retryable(stateful = true)
public void processTransaction() {
// 非幂等操作
}自定义重试策略
RetryTemplate
对于高级用例,您可以定义一个 RetryTemplate Bean 以编程方式处理重试。
示例:
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.retry.policy.SimpleRetryPolicy;
import org.springframework.retry.support.RetryTemplate;
@Configuration
public class RetryConfig {
@Bean
public RetryTemplate retryTemplate() {
RetryTemplate retryTemplate = new RetryTemplate();
// 配置重试策略
SimpleRetryPolicy retryPolicy = new SimpleRetryPolicy();
retryPolicy.setMaxAttempts(5);
retryTemplate.setRetryPolicy(retryPolicy);
return retryTemplate;
}
}Spring Retry 的最佳实践
1. 使用指数退避:通过逐渐增加重试之间的延迟来避免对外部系统造成过大压力。
2. 处理特定异常:避免广泛的异常处理;仅重试临时错误(如 IOException 或 TimeoutException)。
3. 限制重试次数:设置合理的重试次数,以避免不必要的资源消耗。
4. 监控和记录重试:记录重试尝试以便更好地进行可见性和故障排除。
5. 与断路器结合使用:将 Spring Retry 与 Resilience4j 等库结合使用以增强容错能力。
常见用例
1. 外部 API 调用:在服务临时中断或网络错误时重试 API 调用。
2. 数据库操作:在临时连接问题导致失败时重试数据库查询。
3. 消息系统:处理 RabbitMQ 或 Kafka 等系统中的消息传递失败。
4. 文件上传:在间歇性故障时重试文件上传。
常见错误
1. 错误使用 @Retryable 注解:将 @Retryable 放在私有方法或未通过 Spring 管理的代理调用的方法上。
2. 忽略不受支持的异常:未在 @Retryable 的 retryFor 参数中指定需要重试的异常类型。
3. 忘记 @Recover 恢复逻辑:在所有重试尝试失败时没有回退机制。
4. 未正确配置 maxAttempts 和 backoff:重试次数过多或延迟过短/过长,导致性能下降或延迟过长。
5. 忽略线程安全性:在 retryable 方法中使用共享资源(如可变对象)而未确保线程安全。
结论
Spring Retry 为构建弹性的 Spring Boot 应用程序提供了强大的机制。通过利用 @Retryable 和 @Recover 注解,或使用 RetryTemplate 自定义重试策略,开发人员可以优雅地处理临时故障,增强用户体验并保持应用程序的稳定性。





没有回复内容